Ensure medicine safety, compliance, and quality with reliable pharmacy temperature monitoring solutions
Pharmacy Temperature Monitoring
Pharmacy temperature monitoring is essential to ensure the safety, potency, and compliance of drugs, vaccines, and other temperature-sensitive items. Temperature variations as low as a few degrees may result in loss of product efficacy, regulatory non-compliance, and financial loss.
Why Pharmacy Temperature Monitoring is Important
Protecting Medication Quality
- Safeguards medicine potency — Delicate medications such as insulin, vaccines, and antibiotics need to be stored within the recommended temperature range (typically 2°C–8°C) in order to be effective.
- Prevents product deterioration — Minor changes in temperatures can lead to loss of potency, chemical degradation, or contamination hazards, rendering them unsafe for administration to patients.
- Guarantees uniform treatment efficacy — Through proper storage conditions, pharmacies ensure patients receive fully potent and consistent medication.
- Reduces wastage — Effective monitoring avoids wasting expired drugs, which saves costs for pharmacies without compromising on supply continuity.


Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
- Meets international standards of health — Monitoring keeps pharmacies in line with WHO, FDA, and local regulatory standards of medicine storage.
- Easy audit and inspection — Machine logs and reports can be easily forwarded to auditors, minimizing paperwork.
- Avoids penalties and risks — Documentation saves pharmacies from regulatory fines, license suspension, or non-compliance.
- Establishes credibility for the pharmacy — Showcasing compliance enhances the credibility of pharmacies to patients and healthcare authorities.
Reducing Financial Losses
- Avoids expensive spoilage — Regular monitoring catches temperature problems before drugs are rendered useless.
- Safeguards pharmacy profits — By preserving inventory, pharmacies avoid surprise financial blows from spoiled stock.
- Maximizes staff effectiveness — Computer-generated alerts eliminate tedious manual checks, freeing staff to handle customer service and operations.
- Guarantees long-term savings — Less wastage, lower penalties, and effective monitoring result in substantial cost savings in the long term.
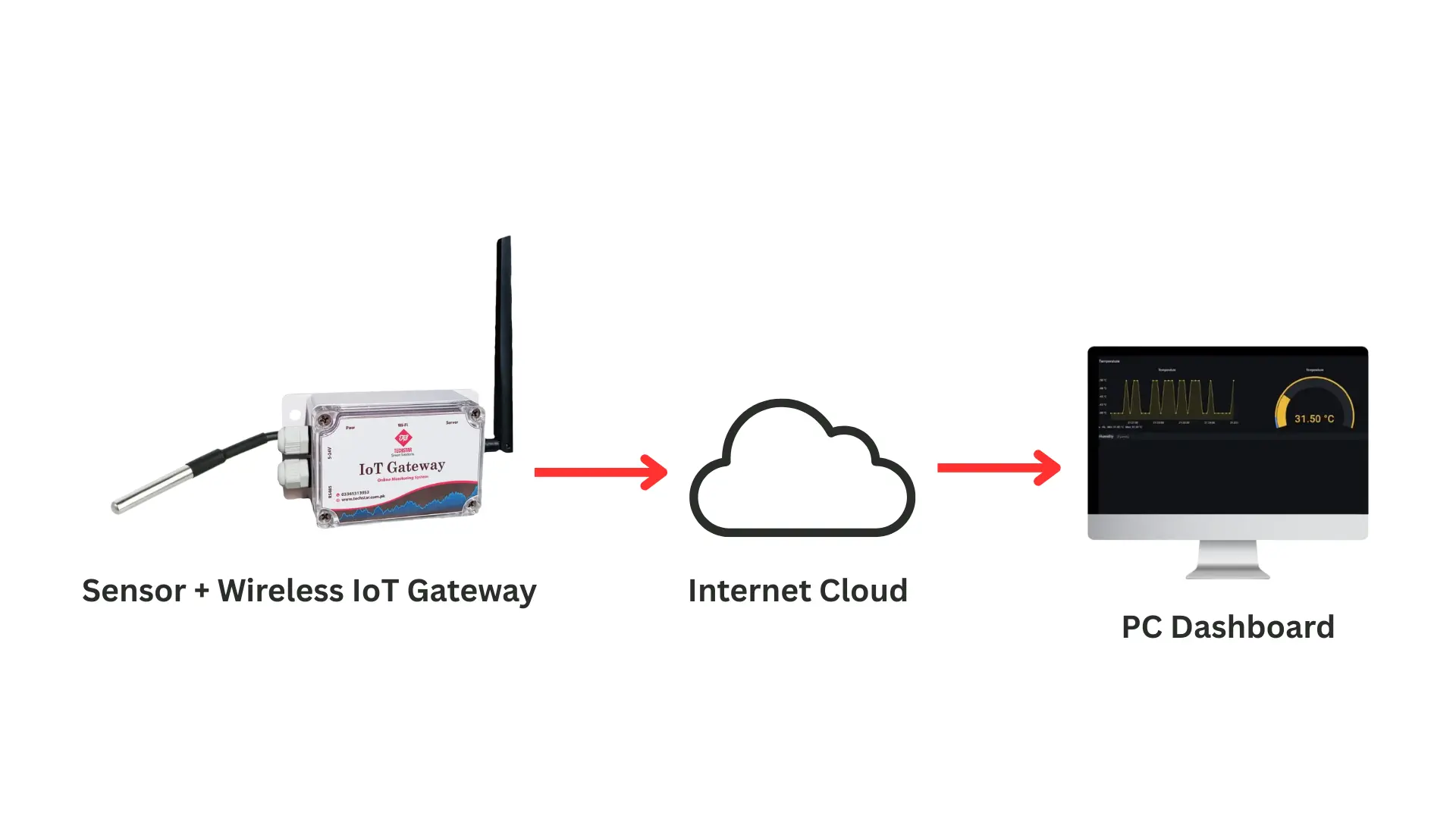
How Pharmacy Temperature Monitoring Works
Pharmacy monitoring systems use wireless sensors and cloud-based dashboards to record and track temperature in real time.
24/7 data logging of refrigerators and storage areas
Email and/or SMS during temperature excursions
Generate reports for audits and compliance
View pharmacy conditions from any location
Real-Time Alerts for Immidiate Action
Our temperature monitoring systems are designed to trigger pharmacy temperature alerts in case of any deviation from the predefined optimal temperature range. These alerts can be sent via SMS, email, or other communication channels, enabling your team to take immediate action before a small issue escalates into a major problem.
Benefits of Digital Pharmacy Temperature Monitoring
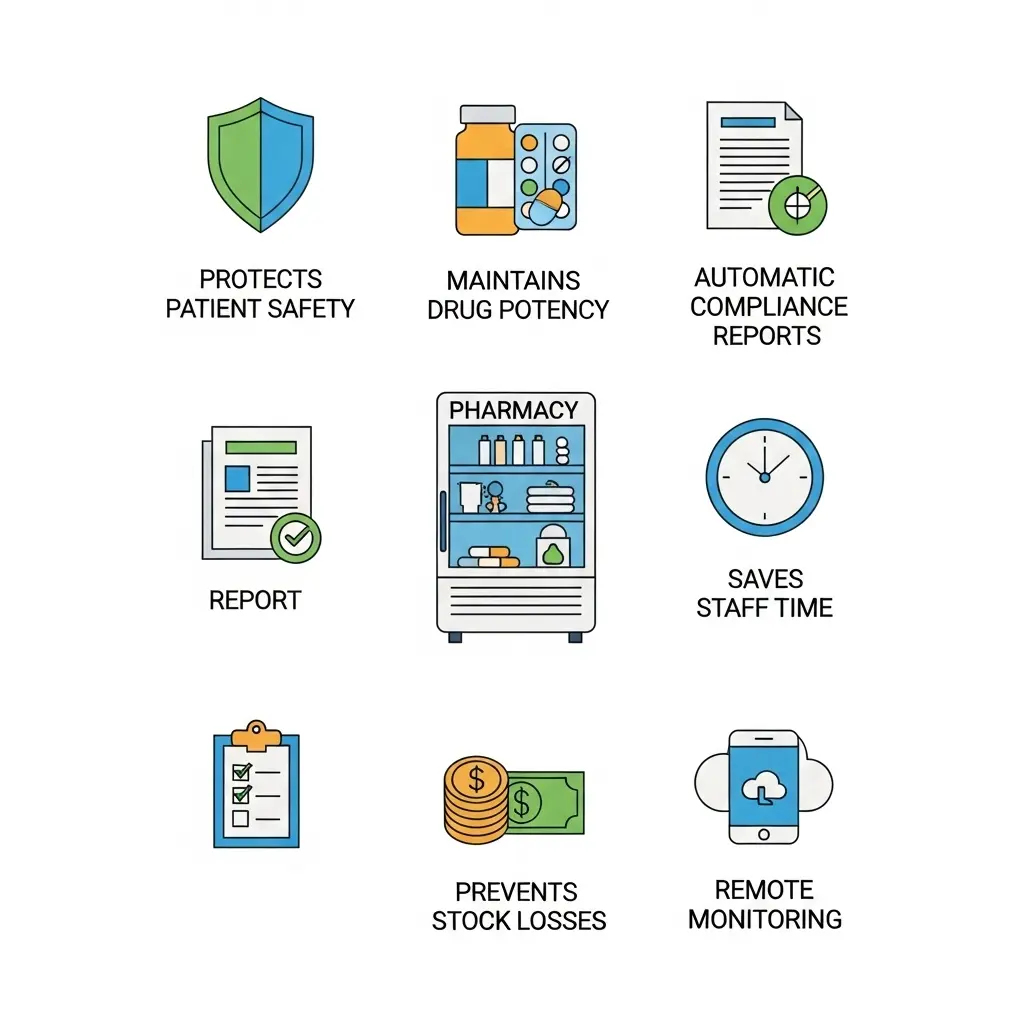
⇒ Protects patient safety
⇒ Maintains drug potency
⇒ Automatic compliance reports
⇒ Saves staff time vs. manual recording
⇒ Prevents costly stock losses
⇒ Provides remote monitoring capability
Applications of Pharmacy Temperature Monitoring
Pharmacy Refrigerators and Freezers
Guarantees medicines, vaccines, and insulin to be stored between the appropriate temperatures
Storage Rooms and Warehouses
Allows controlled storage conditions for pharmaceutical bulk storage
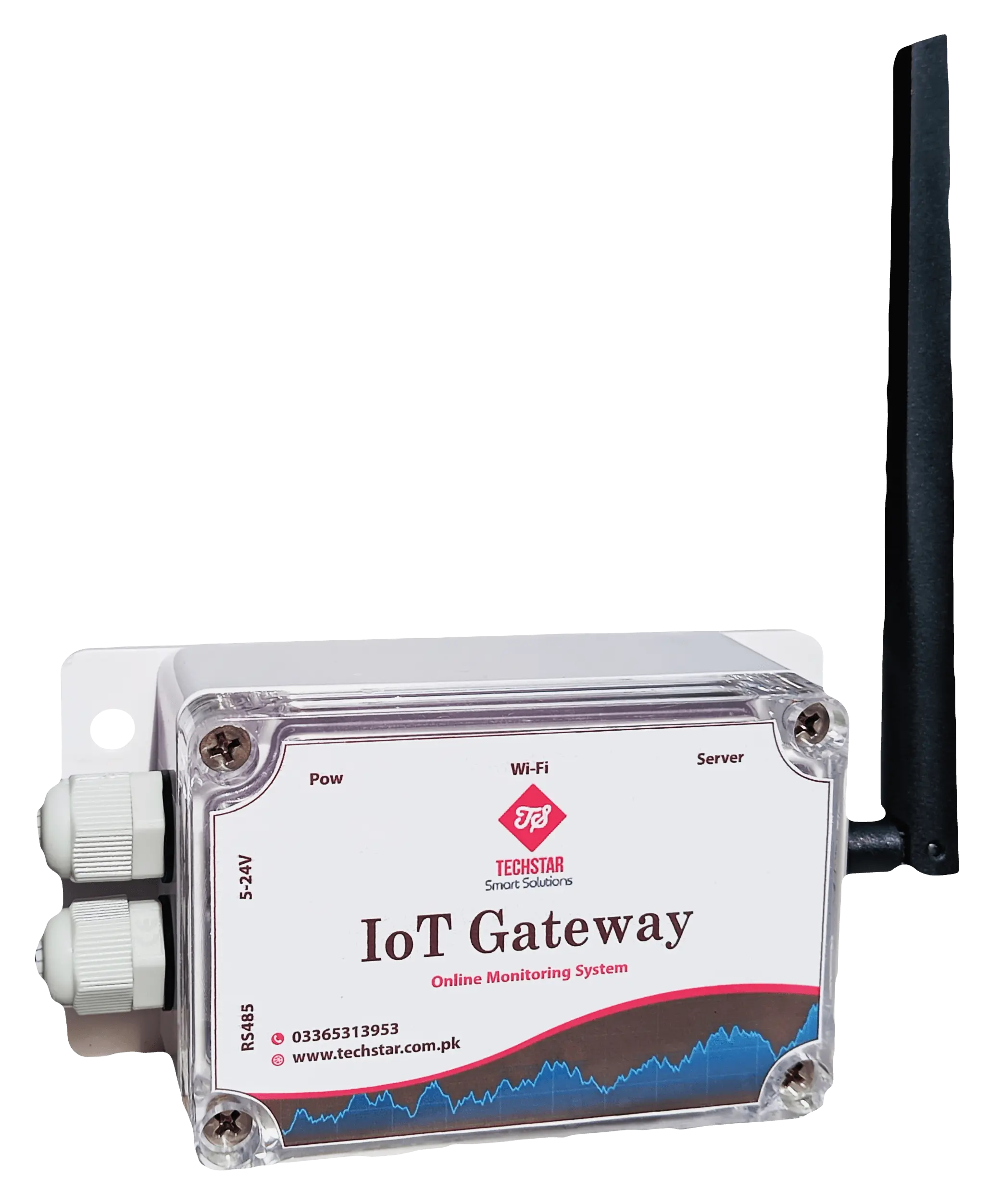


Techstar IoT Gateway Device
Assembled for demanding surroundings, it ensures secure data transmission to the Techstar Cloud. Ideal for industrial, open-air, or pharmacy temperature monitoring applications, this durable gateway combines advanced features with reliable performance.
- External Temperature Sensor
- Techstar Cloud Integration
- Status Indicators
- 5 – 24V DC Permanent Power Supply
- External Wireless Antenna
- Waterproof and Dustproof Enclosure
- Compact Dimensions (132*69*50 mm)
- Imported PCB Fabrication
Comes with Temperature Sensor
- Power: DC 3.3V ~ 5V
- Temperature Range : -10 ~ 100 ℃
- Measuring Precision:±0.5
- Cable length: 0.8 ~ 1.0 m
- Probe size: 2 inches
- Metal probe, with dustproof and waterproof

Online vs. Manual Pharmacy Temperature Monitoring
Feature / Benefit | With Online Monitoring | Without Online Monitoring |
Data Recording | Automatic, 24/7 continuous logging | Manual, time-consuming entries |
Alerts | Instant SMS - Email notification | No alerts – issues found only during manual checks |
Compliance | Automatic reports for audits (WHO, FDA, GSP/GDP) | Risk of missing logs and non-compliance |
Accuracy | High accuracy with calibrated sensors | Human error in manual readings |
Cost Savings | Prevents medicine spoilage and financial losses | High risk of losses due to unnoticed excursions |
Staff Efficiency | Saves time, reduces workload | Staff must record data frequently |
Remote Access | Yes – monitor from anywhere | No – only physical checks possible |
Frequently Asked Questions
The best method to guarantee the security of pharmaceutical products and drugs that can save lives is to use pharmacy temperature monitoring systems. For patients’ safety, it is essential that drugs be stored properly to preserve their effectiveness. Typical components of a pharmacy temperature monitoring system include:
Sensors: These sensors are used to continuously detect temperature in storage spaces such as freezers, refrigerators, and ambient storage.
Alarms & Alerts: Staff members are notified by alarms and alerts if temperatures depart from the predetermined range, enabling prompt action to stop spoiling.
Data reporting and logging: These keep track of temperature data over time, offering a historical record for quality assurance and compliance needs.
Remote Monitoring: By using a computer or smartphone app, pharmacy employees can remotely check temperatures.
Calibration and Compliance: These guarantee precision and adhere to legal mandates, such as those set forth by the FDA or the CDC. Since many items, including vaccinations and some drugs, need to be kept at a precise temperature, temperature monitoring devices are crucial in pharmacies.
Requirements for pharmaceutical temperature monitoring differ based on regulatory bodies and the particular kinds of medications, but often consist of:
Temperature Range and Stability: Manufacturers or regulatory bodies frequently specify the precise temperature ranges for storing pharmaceutical items. Vaccines and other biologics, for instance, need to be refrigerated, usually between 35°F and 46°F.
Continuous Monitoring and Logging: It’s critical to continuously monitor the temperature using precise, calibrated equipment. In order to offer a historical record for quality control and regulatory compliance, this involves taking data at regular intervals.
Alarm Systems: Temperature monitoring in pharmacies should be installed to notify employees of any departures from the ideal temperature range. This will enable prompt remedial action to stop spoiling.
Equipment Validation and Calibration: To guarantee precision and dependability, monitoring equipment should undergo routine validation and calibration.
Mapping and Validation of Storage locations: This may entail temperature mapping and validation procedures to guarantee consistent temperature distribution throughout storage locations.
Regulation Compliance: Following rules established by regulatory agencies such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), or the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Certain reporting guidelines and paperwork may be part of compliance.
Instruction and Protocols: The existence of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for handling temperature excursions and instruction for staff on correct handling and storage techniques, including how to use monitoring equipment.
For the pharmaceutical sector to properly handle and store pharmaceutical items, temperature monitoring requires accurate and trustworthy thermometers. There are several kinds of thermometers that are frequently used:
Because of its precision, usability, and capacity to capture and store data, digital thermometers are utilized to deliver accurate temperature readings.
Digital Thermometers: Because of its precision, usability, and capacity to capture and store data, digital thermometers are utilized to deliver accurate temperature readings.
Infrared Thermometers: Non-contact surface temperature readings are obtained using infrared (IR) thermometers. They are especially helpful when touching the object being measured is unsafe or not possible.
Data Loggers with Temperature Sensors: These gadgets track temperature over time and are perfect for keeping an eye on storage spaces. They are able to offer a thorough record for regulatory compliance and quality assurance.
Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers: Traditional thermometers that can be used in laboratories for particular testing are called liquid-in-glass thermometers. Because of the possibility of breakage and exposure to mercury, their use is decreasing.
Thermocouples: Used in industrial settings, thermocouples can measure temperature at multiple sites at once and are appropriate for a broad range of temperatures.
Bimetallic Thermometers: Ovens and incubators employ bimetallic thermometers, which have a metal strip composed of two distinct metals.
Chart Recorders and Thermographs: These temperature monitoring tools are helpful for keeping an eye on storage conditions because they continuously record temperature measurements throughout time.
Calibrated and Certified Thermometers: Thermometers that have been calibrated and certified in accordance with established criteria are utilized to guarantee accuracy in particular quality control procedures.
The task’s particular requirements, such as the temperature range, required accuracy, feasibility of product contact, and regulatory compliance requirements, all influence the thermometer selection. To guarantee continued accuracy and dependability, these devices must be calibrated and maintained on a regular basis.
A pharmacy’s continuous temperature monitoring device is a system made especially to track and record the temperature of the storage spaces used to hold pharmaceuticals. This gadget makes sure that the items are stored in the best possible circumstances to preserve their safety and effectiveness, especially those that are susceptible to temperature changes, such as vaccines and some pharmaceuticals. Among these gadgets’ key characteristics are:
Continuous Monitoring: Around-the-clock, at predetermined intervals, the gadget continuously measures and logs temperature data.
Alert Systems: It has alert systems to notify employees of temperature variations that surpass predetermined limits, such as text or email messages.
Data Logging and Reporting: In order to comply with regulatory requirements and maintain quality control, the device continuously records temperature data.
Remote Access and Connectivity: A lot of contemporary systems include the ability to monitor temperatures remotely, which enables pharmacy employees to do so frequently in real time from a computer or smartphone.
Calibration and Compliance: Accuracy calibration and adherence to standards established by the FDA, WHO, or other pertinent regulatory bodies are features of the devices.
Integration with HVAC Systems: For automatic climate control, certain cutting-edge systems can be integrated with the pharmacy’s HVAC system.
The particular drugs and goods being kept in a pharmacy will determine the best temperature; different products require varying amounts of storage. The following are general recommendations for typical pharmaceutical storage conditions:
Room Temperature Storage: The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) states that “controlled room temperature,” which is normally between 20°C and 25°C (68°F and 77°F), is the ideal storage temperature for the majority of pharmaceuticals. This range takes into consideration brief fluctuations that could happen during routine handling.
Refrigerated Storage: Certain drugs, such as insulin, biologics, and some vaccinations, need to be kept refrigerated. For refrigerated storage, the typical temperature range is 35°F to 46°F.
Freezer Storage:It may be necessary to keep some things in a freezer. In a pharmacy, freezer storage is usually kept between -13°F and 14°F.
Because every product has different needs, make sure to consult the manufacturer’s exact storage recommendations. To guarantee that these conditions are continuously maintained, pharmacies should make use of continuous temperature monitoring equipment and calibrated thermometers.
Pharmacy Refrigerator Temperature Monitoring
Use a Calibrated Thermometer: Choose a thermometer made especially for refrigerators.
Correct Placement: Place the thermometer in the middle of the refrigerator, away from the walls, door, and cooling components.
Allow Stabilization: Give the thermometer 15 to 30 minutes to get used to the temperature inside.
Regular Checks: For compliance and quality control, check the temperature at least once every day and keep a diary.
Respond to Deviations: Take prompt action and evaluate the safety of medications if temperatures deviate from the advised range.
Maintain Regularly: Make sure the refrigerator is serviced and maintained properly.
Prepare for Emergencies: Make a plan that includes backup storage options in case of refrigerator malfunctions or temperature variations.
To guarantee safe storage, pharmacy freezer and refrigerator temperatures should be monitored and recorded at least once per day. Establish protocols for handling temperature excursions, have continuous monitoring systems with deviation alarms, and calibrate and maintain pharmacy refrigerator temperature monitoring equipment on a regular basis. In hospitals, more regular inspections or sophisticated digital monitoring may be necessary to satisfy regulatory requirements, and staff education regarding appropriate temperature management techniques is essential.
The ideal temperature range for a medication refrigerator in a pharmacy is 35°F to 46°F. The effectiveness and safety of temperature-sensitive drugs, such as vaccines and biologics, are guaranteed by acceptable ranges. To avoid jeopardizing the stored drugs, any departures from the permissible ranges must be swiftly rectified.
A number of characteristics are necessary for efficient biopharma freezer monitoring in order to identify issues early and alert personnel to possible hazards so that prompt remedial action may be implemented. Because they can check the status of the Biopharma freezer remotely from any location, including a computer dashboard or a mobile device, consumers can feel more at ease. Accurate data recording guarantees that industry rules are appropriately observed, allowing employees to react before spoiling happens.
Technology for pharmacy freezer monitoring is made to satisfy the strict operational and regulatory requirements for medicine storage. For efficient pharmacy workflow and medication stability, these systems—as opposed to general-purpose freezer monitors—proactively address temperature variations, generate thorough audit trails, and provide real-time alarms. Unlike other commercial or household freezer systems, pharmacists are able to demonstrate storage integrity to inspectors.
Customizable alert systems are essential for pharmaceutical freezers in order to detect temperature variations. Their adaptability enables pharmacists to act fast to stop costly product loss. Inbuilt logging and reporting tools that monitor outings, changes in humidity, and deteriorated air quality are part of the real-time warnings. While a crucial temperature drop could trigger an alert to the proper emergency contacts, minor changes might only trigger a dashboard message. To safeguard priceless drugs and vaccines, system features provide a robust safety net for pharmacy refrigerator temperature monitoring.
To protect temperature-sensitive medications, pharmacies and medical facilities use remote drug freezer monitoring systems. Employees can receive notifications off-site thanks to the effective Techstar Monitoring System, which records temperature conditions around-the-clock and supports remote access. Clinics, pharmacies, research labs, and hospitals can all benefit from its automated logs and adjustable settings, which enable them to react swiftly to anomalies. Any device may monitor several units, adhering to industry regulations and safeguarding delicate pharmaceuticals.
Years of research and a significant financial investment are necessary to develop a successful medication or vaccination. Protecting the finished product is crucial after spending billions on development. Maintaining these essential medications’ safety, stability, and readiness to help patients in need is made possible by precise temperature monitoring. By combining cutting-edge wireless sensors with real-time data analytics, Techstar Monitoring Systems enable pharmacies maintain drug refrigeration monitoring, which lowers regulatory infractions and product loss.
Preserve priceless medications kept in freezers and refrigerators by:
Preserving Efficacy: Making certain that drugs continue to be useful in treating patients.
Safety Assurance: Preventing medication deterioration that can pose health hazards is known as safety assurance.
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to the stringent storage regulations established by health authorities is known as regulatory compliance.
Financial Protection: Protecting finances by preventing the costly loss of pricey medications.
Reputation Preservation: Preserving the credibility and trustworthiness of healthcare services is known as reputation preservation.
Public Health Impact: Ensuring the wider efficacy of medical interventions, particularly for vaccines and essential medications.

